Incidence and Risk Factors
- Approximately 1 in 20 people may have gall stones.
- About one in three women, and one in six men, form gallstones at some stage in their life.
- The risk of forming gallstones increases with pregnancy, obesity, rapid weight loss.
- However, they cause no symptoms in two out of three people (Asymptomatic gall stone disease)
Understanding the gallbladder and bile
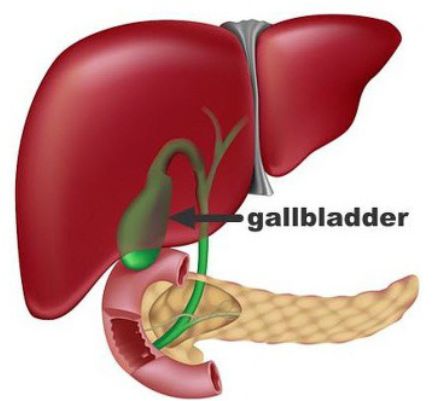
The gallbladder lies under the liver on the right side of the abdomen. It is a 'reservoir' which stores bile. The gallbladder empties the stored bile through the main bile duct into the duodenum.
Bile helps to digest food, particularly fatty foods
What are gallstones?
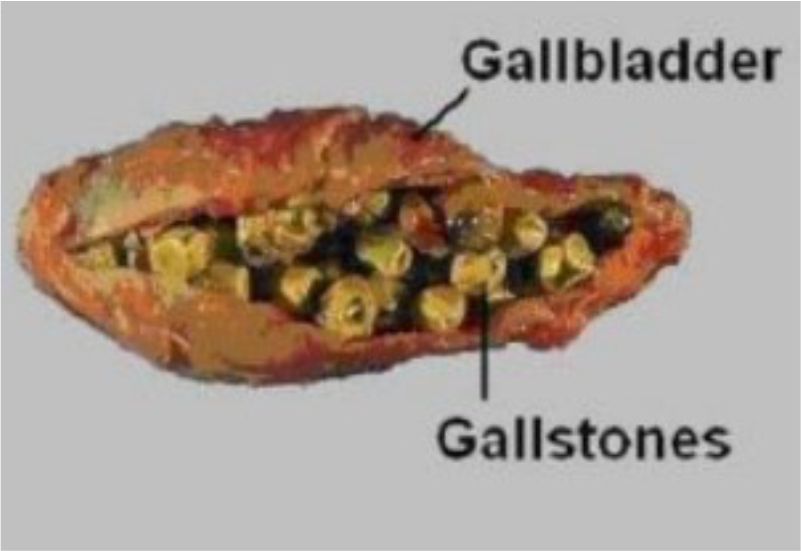
There may be multiple small stones or a single large stone.
What problems can gallstones cause?
Gallstones are often found when the abdomen is scanned for other reasons.- Biliary colic: This is a severe pain in the upper abdomen.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder: This is called cholecystitis. This can lead to infection in the gallbladder. Symptoms usually develop quickly and include abdominal pain, high temperature (fever), and being generally unwell.
- Jaundice: It occurs if a gallstone gets stuck in the bile duct. Bile then cannot pass into the gut and hence causes jaundice
- Pancreatitis: This is an inflammation of the pancreas.
How are gallstones diagnosed?
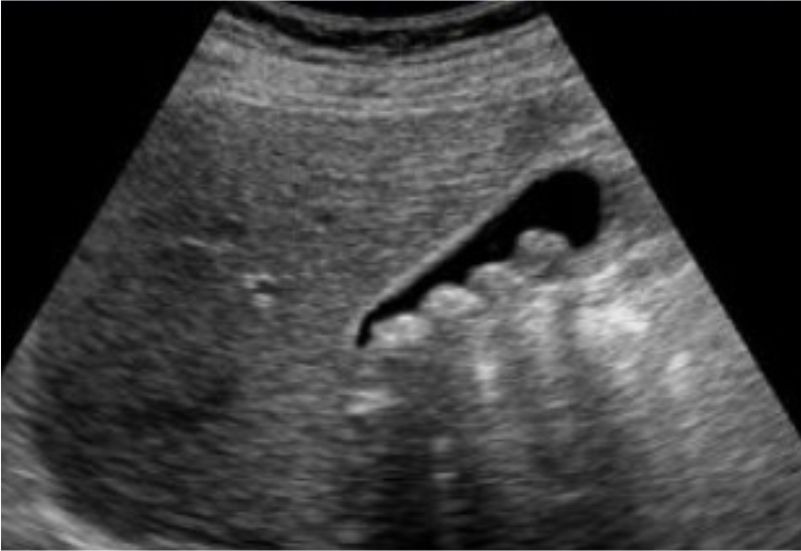
Ultrasound scan and blood tests are the most common investigations done. Other investigations like an MRI (MRCP) and Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) of the abdomen may sometimes be required
What are the treatments for gallstones?
It is often best to leave gallstones alone if there are no symptoms. Symtomatic patients need surgery
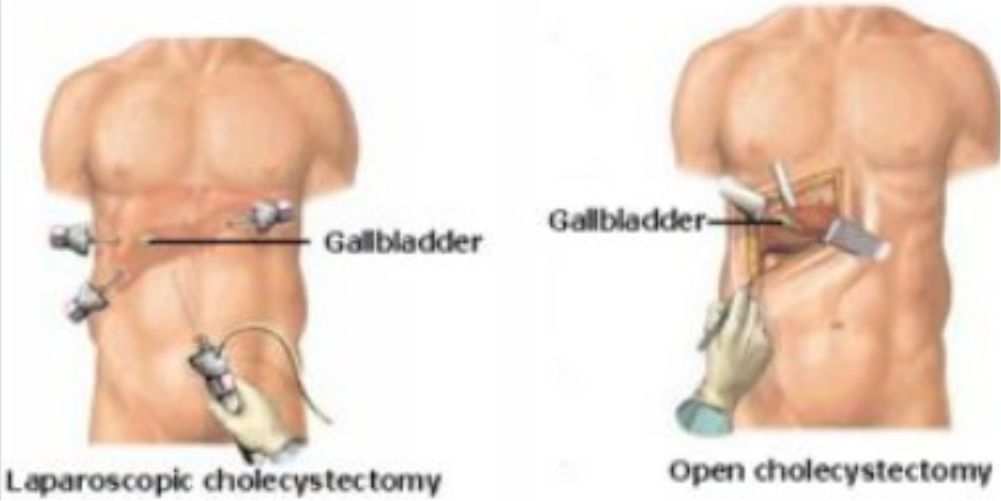
Surgery
- Keyhole surgery is now the most common way to remove a gallbladder. The medical term for this operation is laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
- Rarely, if there are severe adhesions or unsafe to proceed with laparoscopic surgery, the operation may be converted to a traditional open cut method.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS OR COMPLICATIONS OF THE SURGERY?
- Bleeding
- Damage to the blood vessels that go to the liver
- Infection in your belly
- Injury to the common bile duct
- Injury to the small intestine
- Pancreatitis (inflammation in the pancreas)
AFTER THE PROCEDURE
If you do not have any signs of problems, you will be able to go home next day when you are able to drink liquids easily. If there are any problems like bleeding, or the patient is in a lot of pain, or a fever, you may need to stay in the hospital longer
Are there any symptoms after a gallbladder is removed?
Some people who have had their gallbladder removed may develop mild abdominal pain or bloating from time to time.
When will I be able to join work?
You need to take rest for 2-3 days at home (Not bed rest). Most people can join back work within 3-10 days.
Skin stiches would generally dissolve by itself. However, sometimes, sutures may need to be removed after 7-10 days.
